 Overview of experimental design across both studies
Overview of experimental design across both studies
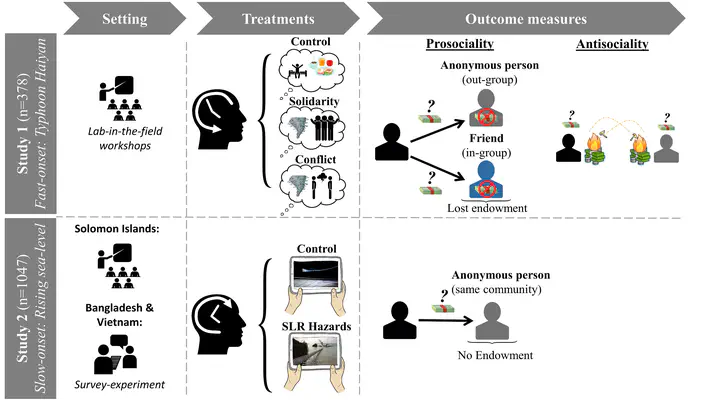
Abstract
People’s willingness to engage in prosocial behavior can affect how vulnerable and resilient populations are to climate hazards. We study how different types of climate hazards, fast-onsetting cyclones and slowly rising sea-levels, might affect peoples’ prosociality using incentivized behavioral tasks. We sample people who are at the forefront of climate change and either experienced Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines (study 1; n=378) or are from sea-level rise hotspots (study 2; n=1047) in Solomon Islands, Bangladesh, and Vietnam. We experimentally manipulate the salience of these hazards through recall or informational videos. Results from study 1 show that increases in prosociality are (i) independent of whether supportive behaviors or conflicts are recalled, (ii) are not only targeted to a narrow in-group, and (iii) do not come with increases in antisocial behaviors. In study 2, we also find that people behave more prosocial when they are informed about the impacts of rising sea-levels. Our survey evidence suggests that people who already perceive the threat of displacement due to rising sea-levels are also more prosocial. Overall, peoples’ responses to both types of hazards are geared towards collective action, which could strengthen their adaptive capacity to deal with climate risks.